One-Time VR Session Found to Reduce Needle Anxiety in Adults
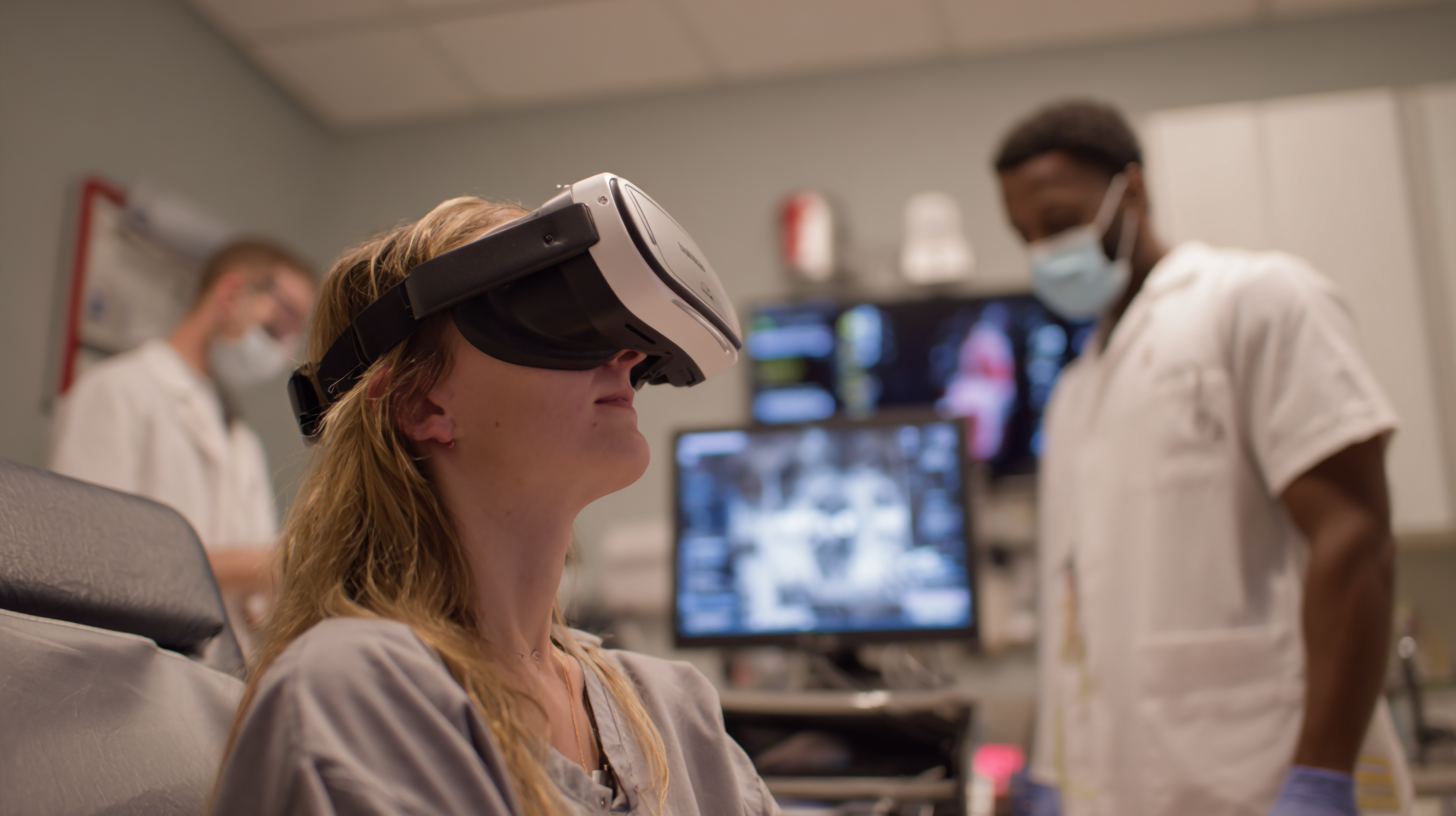
- A peer-reviewed study using XRHealth software found that a single virtual reality session led to statistically significant reductions in needle-related anxiety.
- Participants also rated the VR experience highly for usability and presence, supporting further exploration of immersive exposure therapy.
A new peer-reviewed study in Frontiers in Psychiatry reports that a single virtual reality session can reduce the fear of needles in adults. Researchers from Imperial College London, in collaboration with Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Brown University, observed meaningful anxiety reduction one month after the intervention.
The study used an immersive clinical scenario built with XRHealth software, simulating common medical environments such as waiting rooms and injections. Participants in the experimental group showed improvement on the Specific Phobia Questionnaire and provided high ratings on usability and scenario realism.
"Our research confirms that virtual reality can be a powerful tool for alleviating anxiety in individuals who struggle with needles," said Dr. Nejra van Zalk, Associate Professor and Director of the Design Psychology Lab, Imperial College London, in a press release. "The immersive elements of VR are particularly effective in simulating medical contexts, enabling people to spend time in these environments while remaining secure in the comfort of the 'real world'. VR holds great promise for transforming how we prepare and support people, paving the way toward more compassionate, accessible, and effective healthcare experiences."
With needle anxiety affecting up to 30% of adults, the results highlight virtual reality’s potential as a scalable mental health intervention. The researchers suggest future studies involving larger cohorts and repeated sessions to expand on these findings.
🌀 Tom’s Take:
VR has longstanding roots in mental health, and this study highlights the power of simulation to help people prepare for situations that trigger anxiety.
Source: PRWeb / XRHealth




